Wetland Wednesday
June 17, 2020
As part of the new Navigable Waters Protection Rule the EPA and the US ACOE are developing national standards for classifying perennial and intermittent streams. The EPA defines Streamflow Duration Assessment Methods (SDAMs) as “rapid field assessment methods that use hydrological, geomorphological, and/or biological indicators, observable in a single site visit, to classify streamflow duration as perennial, intermittent, or ephemeral at the reach scale.”
The goal of SDAM is determine if a stream can be classified as perennial, intermittent or ephemeral. The Navigable Waters Protection Rule does not include ephemeral streams as part of its Waters of the US (WotUS) definition. Therefore the SDAM serves as a jurisdictional determinant as well as a stream classification method. Only perennial and intermittent streams are regulated as WotUS.
The SDAM is envisioned to be a regional tool that will have many variations based upon local concerns and priorities. Currently there are five published methodologies that EPA is considering as eligible for its SDAM program. These include:
- SDAM for the Pacific Northwest
- North Carolina Method
- New Mexico Method
- Tennessee Guidance for Hydrologic Determinations
- Fairfax County, Virginia Perennial Stream Field Identification Protocol
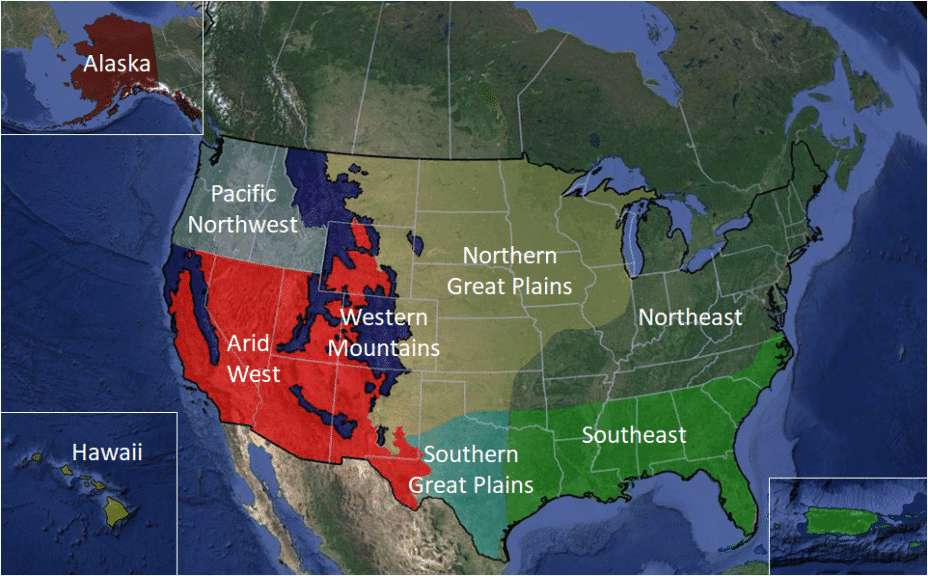
In addition the EPA is expanding the development of SDAMs based upon regional ecological differences. These regions overlap the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Ordinary High Water Mark Scientific Support Document as shown above. In the meantime, the aforementioned methodologies can be used to support a new jurisdictional determination request. Don’t forget these new rules go into effect next week.